
What’s the Best Treatment for Melasma?
Melasma, a common skin condition that causes brown or grayish patches on the face, primarily affects women, especially those in their 20s to 40s. While it can appear anywhere on the face, it is most frequently found on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. Often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy” due to its frequent appearance during pregnancy, melasma is typically triggered by a combination of hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetics. Despite its benign nature, melasma can have a significant impact on one’s self-esteem, leading many to seek effective treatments. But what’s the best treatment for melasma?
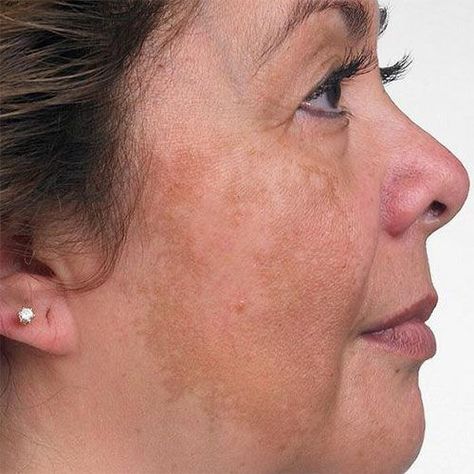
Understanding Melasma: Causes and Triggers
Before diving into treatments, it’s crucial to understand what causes melasma. The condition is caused by the overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color, in certain areas. Several factors contribute to this imbalance:
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, birth control pills, and hormone replacement therapy can increase melanin production, triggering melasma in susceptible individuals.
Sun Exposure: UV rays stimulate the skin to produce more melanin, which can darken existing melasma patches or trigger new ones.
Genetics: A family history of melasma makes individuals more likely to develop the condition.
While melasma is harmless, it can be stubborn and persistent, making it challenging to manage. Fortunately, several treatment options are available to help reduce the appearance of melasma and restore confidence.

Top Treatments for Melasma
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are the first line of defense against melasma. These can include prescription and over-the-counter products that help lighten the skin and even out pigmentation. Common ingredients found in these treatments include:
Hydroquinone: This is the most widely used and effective lightening agent for melasma. It works by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which plays a key role in melanin production. Hydroquinone is available in both prescription strength (4%) and over-the-counter strength (2%).
Retinoids (Retinol and Tretinoin): Retinoids are known for their ability to speed up cell turnover, allowing for faster skin regeneration and helping fade dark spots. Tretinoin, a prescription-strength retinoid, is particularly effective but can cause irritation, especially when used in conjunction with other products like hydroquinone.
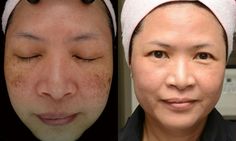
And if you are looking for these two wonders, it is not difficult anymore. Visit our shop and get the best deals at this link :
Vitamin C: Known for its antioxidant properties, Vitamin C helps brighten the skin by inhibiting melanin production and reducing oxidative stress. It can be used alongside other treatments for enhanced results.
Azelaic Acid: This naturally occurring acid helps reduce pigmentation by inhibiting melanin production. It’s often recommended for those with sensitive skin since it is gentler than other ingredients like hydroquinone and retinoids.
Kojic Acid: Similar to hydroquinone, kojic acid inhibits melanin production and can be found in many skin-lightening products.
While these ingredients can significantly reduce the appearance of melasma, they require consistent application, typically over a period of several weeks to months, before visible results appear.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes the top layer to peel off, revealing fresher, more even-toned skin underneath. A variety of acids, including glycolic acid, salicylic acid, and trichloroacetic acid (TCA), are used in chemical peels to exfoliate the skin and target pigmentation.
Chemical peels can be an effective treatment for melasma, particularly for individuals with deeper, more stubborn pigmentation. However, they should be performed by a qualified dermatologist to avoid side effects like irritation or scarring. Some people may experience a temporary darkening of pigmentation, known as “post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation,” before improvement is seen.

Laser Therapy
Laser treatments, including fractional lasers and intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy, are increasingly popular for treating melasma. These treatments work by targeting melanin in the skin with concentrated light energy, breaking it down and allowing the body to naturally eliminate it.
Fractional Lasers: These lasers deliver light in microscopic beams that penetrate the skin, targeting pigmentation while minimizing damage to surrounding tissue. They are effective for treating deep melasma patches.
IPL (Intense Pulsed Light): IPL uses broad-spectrum light to target pigment and reduce discoloration. IPL is often less aggressive than fractional lasers, making it suitable for more superficial melasma.
While laser treatments can offer significant results, they can be expensive, and there’s a risk of side effects, including worsening pigmentation or scarring, especially for individuals with darker skin types. It’s important to consult with a skilled practitioner to determine the most suitable option for your skin.
Sun Protection
Regardless of the treatment chosen, sun protection is essential in managing melasma. UV exposure is a major trigger for melasma, and without proper protection, the condition can worsen or return after treatment. Key steps to protect the skin include:
Using a Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Choose a sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Apply it generously to all exposed areas of the skin and reapply every two hours when outdoors.
Wearing Protective Clothing: Hats, sunglasses, and clothing with UPF (ultraviolet protection factor) can provide additional defense against UV radiation.
Seeking Shade: Avoid direct sun exposure, especially during peak hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
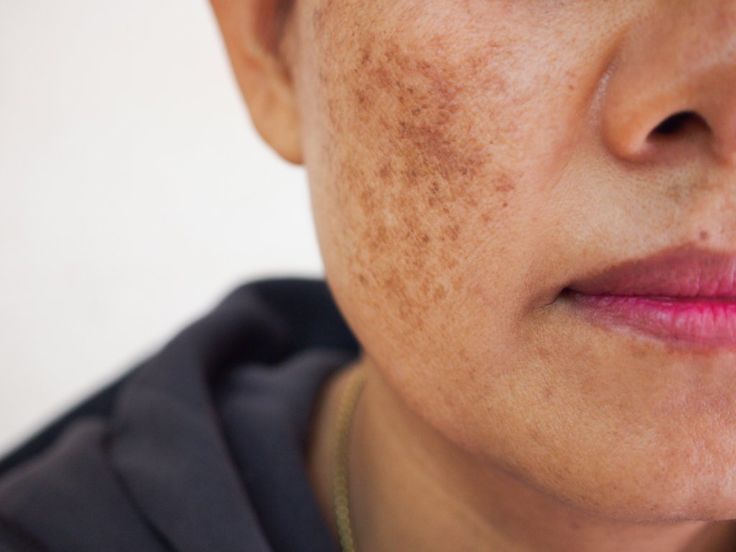
Lifestyle Modifications
Along with medical treatments, making certain lifestyle changes can help manage melasma. This includes:
Avoiding Hormonal Triggers: If melasma is linked to hormonal changes, it may be helpful to discuss alternative birth control methods with a doctor or avoid hormone therapy when possible.
Maintaining a Healthy Skin Care Routine: Use gentle, non-comedogenic skincare products to avoid irritating the skin and worsening pigmentation. Incorporate moisturizing and soothing ingredients like aloe vera and ceramides.
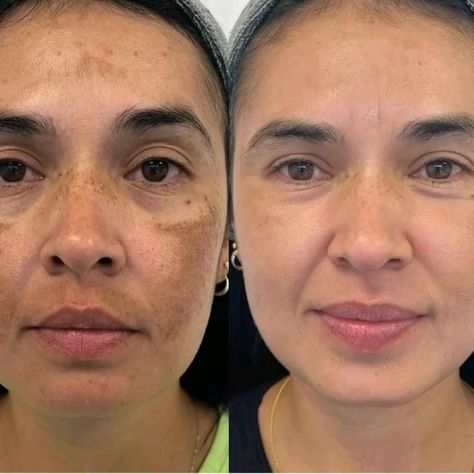
While melasma can be challenging to treat, there are effective options available to help reduce pigmentation and restore even skin tone. Topical treatments such as hydroquinone, retinoids, and Vitamin C are often the first choice, while more intensive options like chemical peels, laser treatments, and IPL can offer significant improvement for stubborn cases. Regardless of the treatment, maintaining diligent sun protection and making lifestyle modifications are key to preventing melasma from reoccurring.
Consulting with a dermatologist is essential to develop a tailored treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and skin type. With the right approach, melasma can be managed effectively, allowing you to achieve clearer, more radiant skin.
