Types of acne, Causes, and Effective Treatments
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions affecting people worldwide, especially teenagers and young adults. Though it is often seen as just a cosmetic issue, acne can have a significant impact on self-esteem and mental well-being. The good news is that with proper care and treatment, acne can be managed effectively. This article will explore the different types of acne, their causes, and the best ways to care for acne-prone skin.
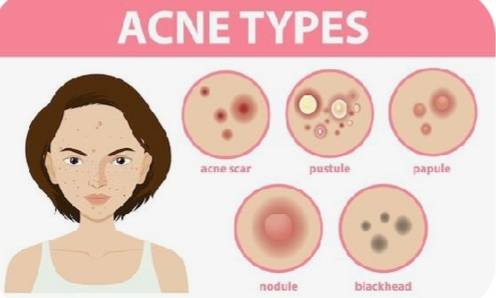
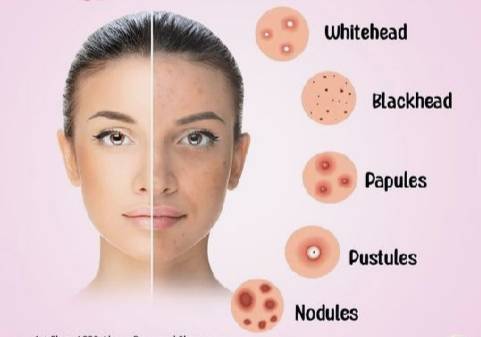
Types of Acne
Acne can appear in various forms, ranging from small blackheads to deep, painful cysts. Understanding the different types of acne can help in selecting the most appropriate treatment. Here are the primary types:
- Blackheads (Open Comedones): Blackheads are small, dark spots that appear on the skin, often on the nose and forehead. They form when pores become clogged with excess oil and dead skin cells. The dark color is due to oxidation, not dirt, which occurs when the contents of the pore are exposed to air.
- Whiteheads (Closed Comedones): Whiteheads are similar to blackheads but remain closed. The pore is blocked by oil and dead skin, and because it doesn’t come in contact with air, the contents stay white or flesh-colored.
- Papules: Papules are small, red, raised bumps that appear on the skin. They are typically tender to the touch and can become inflamed. They occur when the walls of clogged pores break, leading to mild inflammation.
- Pustules: Pustules are similar to papules but contain pus. They are red at the base with a white or yellow center. They are a result of the immune system’s response to the bacterial infection in the clogged pore.
- Nodules: Nodules are large, hard, painful lumps beneath the skin’s surface. They form when the infection in the pore goes deeper into the skin. Nodules are often difficult to treat and may cause scarring.
- Cysts: Cysts are the most severe form of acne. They are large, painful, and filled with pus. Cysts can cause significant scarring and are often a result of a more intense bacterial infection. These require professional treatment, often including prescription medications or even drainage.
Causes of Acne
Acne is caused by a combination of factors, primarily affecting the sebaceous (oil) glands in the skin. Here are the most common causes:
- Excess Sebum Production: The sebaceous glands produce sebum, an oily substance that helps keep the skin moisturized. However, an overproduction of sebum can clog pores, providing a breeding ground for acne-causing bacteria.
- Clogged Pores: When pores become blocked with excess oil, dead skin cells, or dirt, they can lead to blackheads, whiteheads, or more severe forms of acne.
- Bacteria: The bacteria Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) thrive in clogged pores and can cause inflammation, leading to pimples and cysts.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or the use of birth control, can increase sebum production, making acne more likely.
- Diet and Lifestyle: While the link between diet and acne is still debated, some studies suggest that high-glycemic foods (like sugary snacks) and dairy may contribute to acne. Additionally, stress, lack of sleep, and smoking can exacerbate acne outbreaks.
- Genetics: Acne can run in families, so if your parents had acne, you might be more prone to developing it as well.

And if you are looking for these two wonders, it is not difficult anymore. Visit our shop and get the best deals at this link :
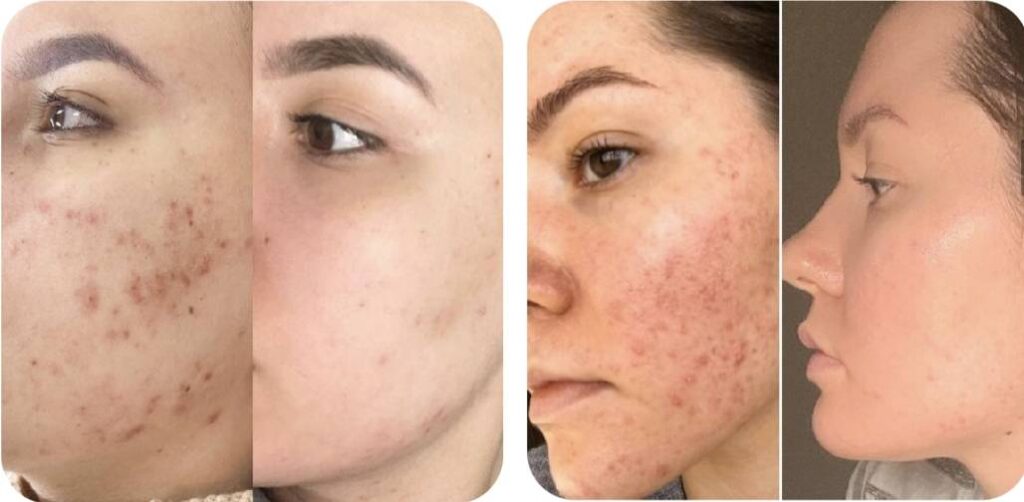
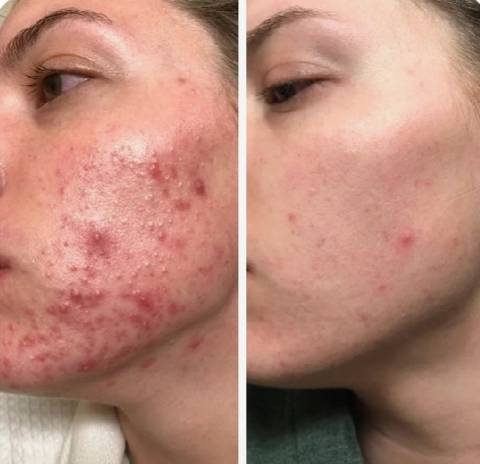
Tips for Caring for Acne-Prone Skin
Effective acne treatment involves a combination of proper skincare habits, healthy lifestyle choices, and sometimes medical intervention. Here are the best practices for managing acne:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser to wash your face twice daily—once in the morning and once before bedtime. Avoid harsh scrubbing, as this can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter acne treatments containing ingredients such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or sulfur can help reduce acne. These ingredients target the bacteria, unclog pores, and reduce inflammation.
- Moisturize: Even if you have oily skin, it’s essential to use an oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated. This prevents the skin from producing excess oil to compensate for dehydration.
- Avoid Picking or Squeezing: Picking at acne can push bacteria deeper into the skin, leading to more severe breakouts and scarring. It’s important to let pimples heal naturally.
- Use Sunscreen: Acne treatments can make the skin more sensitive to sunlight, so applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily is vital to protect the skin and prevent pigmentation.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall skin health. Consider reducing your intake of sugary and dairy products, as they may trigger acne flare-ups in some individuals.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If acne persists or becomes severe, consulting a dermatologist is essential. They can prescribe stronger medications, such as topical retinoids, antibiotics, or even oral medications like Accutane for cystic acne.
Acne is a common and often frustrating skin condition, but with the right approach, it can be managed effectively. By understanding the types and causes of acne, adopting a consistent skincare routine, and making healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can minimize outbreaks and maintain clearer skin. If over-the-counter treatments don’t suffice, consulting a dermatologist can provide more tailored solutions. Remember, healthy skin requires patience and care, and effective treatments are available for everyone.
